RabbitMQ 기초
2018-02-04
RabbitMQ는 메시지 브로커의 한 종류로, 얼랭으로 만들었다.
또 다른 메시지 브로커인 Kafka와 자주 비교되는데, AMQP 등의 표준 프로토콜 지원, ZooKeeper 같은 코디네이터가 필요없다는 점, 메시지 priority 설정, 웹 콘솔 지원 등이 장점으로 꼽힌다.
여기서는 rabbitmqadmin 명령으로 콘솔에서 메시지를 보내고(publish) 가져오고(consume), 동일한 작업을 파이썬 코드로도 실행해 본다.
Exchange, Binding, Queue
먼저, RabbitMQ의 핵심 구성 요소인 Exchange, Binding, Queue에 대해 짚고 넘어가자. 아래 그림은 RabbitMQ 호스팅 서비스인 CloudAMQP에서 가져왔다.
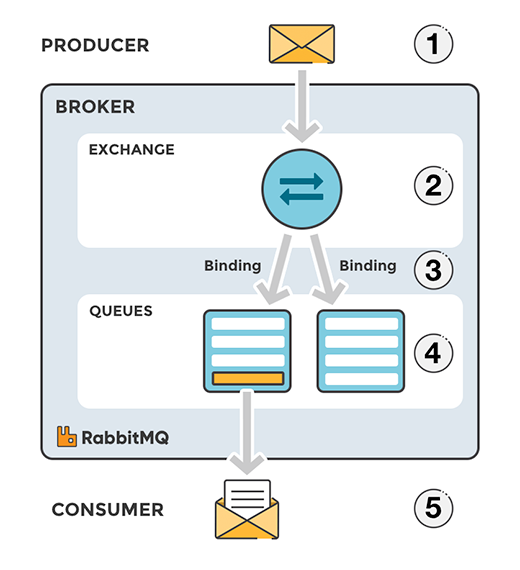
프로듀서 ①이 RabbitMQ의 익스체인지에 메시지를 전송한다.
RabbitMQ 메시지 처리 모델의 중요 원칙은 프로듀서가 어떤 메시지도 큐에 직접 보낼 수 없도록 하는 것이다. 프로듀서는 오직 익스체인지에만 메시지를 보낼 수 있다.
익스체인지 ②가 수신한 메시지는 바인딩 ③을 통해 큐 ④로 들어간다.
바인딩은 익스체인지와 큐의 관계를 정의한 것으로 라우팅과 같은 개념이다.
큐는 메시지가 저장되는 버퍼다.
마지막으로, 컨슈머 ⑤가 메시지를 가져와 처리한다.
rabbitmqadmin
RabbitMQ를 설치한 후에, 추가로 해야 될 작업은 rabbitmqadmin 명령행 설치다.
웹 콘솔을 통해 설치하면 되는데 찾기가 힘들 뿐, 설치는 간단하므로 아래 링크를 참고하자.
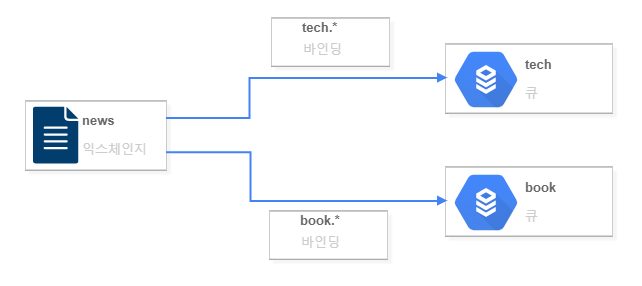
예제로 사용할 메시징 처리 흐름은 아래와 같다.
news라는 익스체인지에 메시지를 보내면, 메시지 id prefix를 기준으로 하는 바인딩을 통해, tech와 book 큐로 각각 전달된다.
익스체인지를 생성한다.
$ rabbitmqadmin declare exchange name=news type=topic
큐를 생성한다.
$ rabbitmqadmin declare queue name=tech
$ rabbitmqadmin declare queue name=book
생성한 큐 목록을 확인한다.
hyun@hyun-VirtualBox:~$ rabbitmqadmin list queues
+------+----------+
| name | messages |
+------+----------+
| book | 0 |
| tech | 0 |
+------+----------+
바인딩을 생성한다.
$ rabbitmqadmin declare binding source="news" destination_type="queue" destination="tech" routing_key="tech.*"
$ rabbitmqadmin declare binding source="news" destination_type="queue" destination="book" routing_key="book.*"
바인딩 생성 후, 목록을 확인하자.
hyun@hyun-VirtualBox:~$ rabbitmqadmin list bindings
+--------+-------------+-------------+
| source | destination | routing_key |
+--------+-------------+-------------+
| news | book | book.* |
| news | tech | tech.* |
+--------+-------------+-------------+
이제, news 익스체인지에 전송된 메시지 중, 메시지 id가 book.*에 매칭되면 book 큐에 저장되고, 메시지 id가 tech.*에 매칭되면 tech 큐에 저장된다.
콘솔에서 메시지를 전송해 보자.
hyun@hyun-VirtualBox:~$ rabbitmqadmin publish exchange=news routing_key="tech.12" payload="12번째 뉴스 - 러스트"
Message published
news익스체인지에 메시지 id를 tech.12로 설정해서 보냈으므로, tech 큐에 저장됐을 것이다. 확인해 보자.
hyun@hyun-VirtualBox:~$ rabbitmqadmin list queues
+------+----------+
| name | messages |
+------+----------+
| book | 0 |
| tech | 1 |
+------+----------+
이번에는 tech 큐에 저장된 메시지를 가져온다.
hyun@hyun-VirtualBox:~$ rabbitmqadmin get queue=tech requeue=false
끝의 requeue 옵션은 메시지를 큐에서 꺼내 온 다음, 다시 큐에 저장할 것인지를 지정하는 옵션이다.
디폴트 동작은 requeue=true로, 메시지를 꺼내와도 삭제되지 않고, 큐에 메시지가 다시 저장된다.
여기서는 requeue=false로 가져왔으므로, 이 명령이 실행되면 큐에서 메시지가 사라져야 한다.
확인해 보자.
hyun@hyun-VirtualBox:~$ rabbitmqadmin list queues
+------+----------+
| name | messages |
+------+----------+
| book | 0 |
| tech | 0 |
+------+----------+
파이썬 스크립트
이번에는 rabbitmqadmin 대신, 파이썬 코드로 메시지를 게시하고 가져와 본다.
파이썬에 pika를 설치해줘야 한다. pika는 RabbitMQ가 사용하는 AMQP 라이브러리다.
먼저, tech 메시지를 수신하는 consumer.py 코드다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# consumer.py
import pika
from pika import BlockingConnection, BasicProperties
def on_message(channel, method_frame, header_frame, body):
tech_id = method_frame.routing_key.split('.')[-1]
print('---새 메시지---')
print('tech id : ', tech_id)
print('body : ', body.decode('utf-8'))
channel.basic_ack(delivery_tag=method_frame.delivery_tag)
print("tech 메시지 수신 대기 중...\n")
connection = pika.BlockingConnection()
channel = connection.channel()
channel.basic_consume(on_message, queue='tech')
try:
channel.start_consuming()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
channel.stop_consuming()
connection.close()
로컬 rabbitmq에서 동기식 연결을 맺고 tech.* 메시지가 수신되면 가져온다. 메시지를 가져 온 다음, ack를 보내서 큐에서 메시지가 제거되도록 한다.
다음으로, 메시지를 보내는 publisher.py 코드다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# publisher.py
from pika import BlockingConnection, BasicProperties
def message(topic, message):
connection = BlockingConnection()
try:
channel = connection.channel()
props = BasicProperties(content_type='text/plain', delivery_mode=1)
channel.basic_publish('news', topic, message, props)
finally:
connection.close()
message('tech.17', 'ejabberd 버전업')
consumer.py를 실행시켜 두고, 다른 쉘에서 publisher.py를 실행했을 때 출력은 다음과 같다.
(work) hyun@hyun-VirtualBox:~/work/python$ python consumer.py
tech 메시지 수신 대기 중...
---새 메시지---
tech id : 17
body : ejabberd 버전업